Size Matters: A Comparison of Small and Large Food Processing Equipment
Choosing the right equipment is crucial in the food processing industry. As businesses grow and production demands change, food processing equipment becomes more diverse in type and scale. Both small and large food processing machines offer distinct advantages and limitations. Whether you are a startup or a well-established factory, understanding the differences between these two types of equipment is vital for optimizing production efficiency, controlling costs, and enhancing product quality.

1. Pros and Cons of Small Food Processing Equipment
1.1 Advantages
A. Small Footprint
Small food processing equiment is typically designed to be compact, making it ideal for businesses with limited space. For startups, small workshops, or even home-based food processing businesses, small equipment offers a space-efficient solution. These machines can perform multiple tasks within a limited area, maximizing the use of available space.
B. Easy to Operate
Small equipment is generally simpler to operate, requiring less technical knowledge. The user-friendly design ensures that operators can quickly learn to use the equipment, reducing the need for extensive training. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with inexperienced staff, as it cuts down on training costs.
C. Lower Initial Investment
Compared to large machines, small food processing equipment typically comes with a lower price tag, making it a great option for businesses with limited budgets. The reduced initial investment allows companies to start production without significant financial strain. Additionally, maintenance costs for small machines are also lower, making them a more economical option in the long term.
D. High Flexibility
Small machines are ideal for diversified production, allowing quick adaptation to different product processing requirements. Users can switch between different processing modes in a short amount of time, catering to different types of raw materials or products. This high level of flexibility is particularly useful for companies producing a wide range of products but in smaller quantities.
1.2 Disadvantages
A. Limited Production Capacity
Due to their size, small food processing machines cannot meet the demands of high-volume production. In cases where large quantities are needed, using small machines may result in extended production times, reducing overall productivity and efficiency.
B. Limited Functionality
Small machines often have limited functionality. Unlike large equipment, they cannot handle complex production processes that require multiple functions. For example, a small mixer might only handle basic mixing operations, whereas more sophisticated machines can perform a variety of tasks in one unit.
C. Low Scalability
As businesses grow, the limitations of small machines become more apparent. When production needs increase, small equipment may not be sufficient to meet demand, leading to the need for new or additional machinery, which adds to costs.
2. Pros and Cons of Large Food Processing Equipment
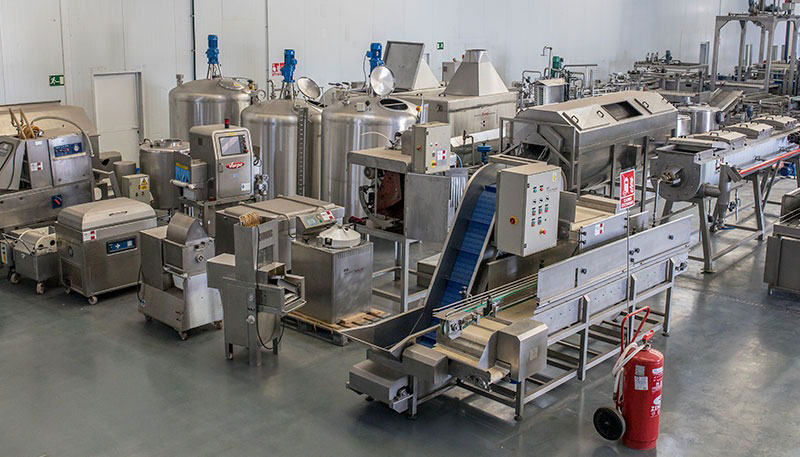

2.1 Advantages
A. High Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of large food processing machines is their high production capacity. Whether handling everyday high-volume production or meeting sudden order demands, large machines can efficiently handle large quantities of raw materials. With their high processing speed, businesses can produce more in less time, significantly improving production efficiency.
B. Multifunctionality
Large equipment often incorporates multiple functions, allowing businesses to complete several steps of the processing workflow with a single machine. For example, a large machine may be able to cut, mix, and package food products in one go. This reduces the time spent transitioning between different pieces of equipment and boosts overall productivity.
C. High Degree of Automation
Many large food processing machines come with advanced automation systems, reducing the need for manual intervention. These automated systems improve precision in production, ensuring consistency in product quality. In long-term operations, automation can help reduce labor costs as fewer workers are required to operate the machinery.
D. Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Although large machines require a higher initial investment, their efficiency and durability make them a sound long-term investment. High-quality large equipment can serve businesses for many years, providing the necessary capacity for growth while minimizing the need for frequent replacements or upgrades.
2.2 Disadvantages
A. Large Space Requirements
Large machines often have substantial size requirements, needing ample space for installation and operation. For businesses with limited factory space, large equipment may not be a practical option. Moreover, adjusting production lines that incorporate large machines can be challenging due to their size and the complexity of moving or reconfiguring them.
B. High Initial Investment
The upfront cost of large food processing machines is considerably higher than that of smaller machines. Businesses must carefully plan their budget to ensure they can afford the equipment. Additionally, the maintenance and operational costs for large machines are also higher, including power consumption and routine servicing.
C. Complex Operation
Large machines, while highly automated, often require skilled operators to manage them effectively. Training employees to use these machines can be time-consuming and costly. In addition, when these machines break down, the complexity of repairs often means higher repair costs and longer downtimes.
D. Low Flexibility
Large machines are typically designed for high-volume, single-type production. Adjusting them to process different products or materials can be difficult and time-consuming, limiting their flexibility in diversified production scenarios. For companies that frequently change their product lineup, large machines may not offer the adaptability they need.
3. Detailed Comparison of Small and Large Food Processing Equipment
| Comparison Point | Small Food Processing Equipment | Large Food Processing Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Space Requirements | Small footprint, suitable for limited spaces | Requires a large area, best for larger factories |
| Production Capacity | Limited production capacity | High production efficiency, suitable for large batches |
| Functionality | Limited to single tasks | Multifunctional, can perform various tasks in one machine |
| Investment Cost | Lower initial cost and maintenance | High upfront investment, long-term cost-efficient |
| Operational Complexity | Easy to operate, minimal training required | Complex, requires skilled operators and training |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good for small-batch production | Low flexibility, best for consistent, high-volume production |
| Automation Level | Low automation, more reliant on manual operation | Highly automated, reduces manual labor |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, hard to expand production | High scalability, suitable for long-term growth |
| Maintenance | Simple to maintain, low cost | Complex maintenance, higher costs for repairs |
4. How to Choose the Right Food Processing Equipment?
4.1 Business Size and Production Needs
When selecting equipment, businesses must consider their production scale. If you’re a startup or a small workshop, small equipment is likely to meet your needs at a lower cost. On the other hand, large factories with high production demands will benefit more from large machines due to their efficiency and production capacity.
4.2 Budget
Budget is a crucial factor in deciding which type of equipment to choose. Small machines offer a low-cost entry point, but their capacity might limit future growth. Large machines, while more expensive upfront, provide a better return on investment over the long term if you plan to scale quickly.
4.3 Product Variety
Different food products have different processing requirements. If your business deals with a wide range of products, small equipment offers greater flexibility for frequent changes. However, if your production focuses on a limited range of products with consistent demand, large machines will significantly boost your output.
4.4 Maintenance and After-Sales Support
Large machines often require specialized maintenance, so it’s essential to choose a supplier that offers reliable after-sales support. For small equipment, while maintenance is simpler, it’s still important to ensure that the machine’s parts are durable and that regular maintenance is performed to keep the equipment running smoothly.
5. Conclusion
Choosing the right food processing equipment is critical for maximizing production efficiency and long-term business growth. Small machines offer greater flexibility, easier operation, and lower initial costs, making them ideal for small-scale, diversified production. On the other hand, large machines provide higher production capacity, advanced automation, and better long-term cost efficiency, which suits larger businesses with consistent, high-volume production needs. By carefully considering your business size, product requirements, budget, and maintenance needs, you can make the right choice and set your company on a path to success.

How to choose food processing equipment that suits your needs?
Sure, here are the steps and considerations for choosing food processing equipment suitable for your needs, translated into English:
Determine Your Needs:
Budget:
Type of Equipment:
Production Scale:
Level of Automation:
Energy Efficiency:
Durability and Maintenance:
Hygiene Standards:
Supplier Reputation:
Warranty and After-Sales Service:
Scalability:
Trial and Demonstration:
Compare Quotes:
Consider Used Equipment:
Consult Industry Experts:
Check Regulatory Compliance:
Consider Future Trends:
Clearly define your production requirements, including product types, production volume, and desired production speed.
Establish the budget you are willing to allocate for the equipment.
Based on your product types, determine the types of equipment needed, such as cutters, mixers, baking equipment, packaging machines, etc.
Choose between small, medium, or large equipment based on your production scale.
Consider the level of automation of the equipment; automated equipment can increase efficiency but at a higher cost.
Opt for energy-efficient equipment to reduce long-term operating costs.
Choose equipment that is durable and has low maintenance costs.
Ensure the equipment meets food safety and hygiene standards.
Select suppliers with a good reputation to ensure after-sales service and technical support.
Understand the warranty terms and after-sales service for the equipment.
Consider future expansion needs and choose equipment that can be upgraded or expanded.
If possible, request a trial or demonstration of the equipment from the supplier.
Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers and compare them.
If the budget is limited, consider purchasing well-maintained used equipment.
Consult industry experts or peers for their advice and recommendations.
Ensure the selected equipment complies with local regulations and industry standards.
Consider industry trends and choose equipment that is not likely to become obsolete in the next few years.
By following these steps, you can more systematically evaluate and select food processing equipment that meets your needs.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner










 Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line Automatic Rice Production Line
Automatic Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?